When naming files, you use tags as placeholders for system and column values.
System values
There are 2 system values you can use, the current row number, and the column number. Row numbers are indicated by the <%row%> tag, and column number by the <%columm%> tag e.g.
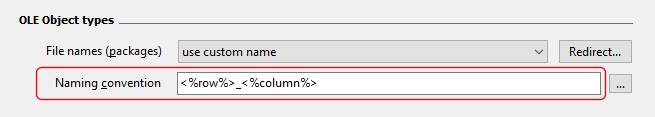
You can add format specifiers to both these system values as they are numeric values. See below for details.
You can also use the <%package_file_name%> tag to use the original file name of an embedded OLE package. The product automatically uses only the file name portion of the value.
Column values
To use a value from a table or query column, enter the name of the column enclosed in square brackets. For e.g. if you had the following table structure:
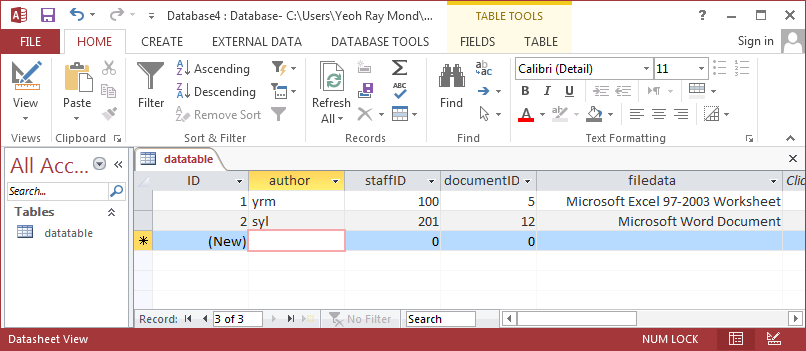
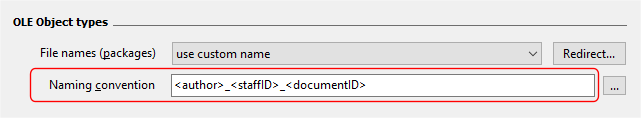
and you wanted to name the exported files using the author, staffID, and documentID values, you can use the following naming convention:
Format specifiers
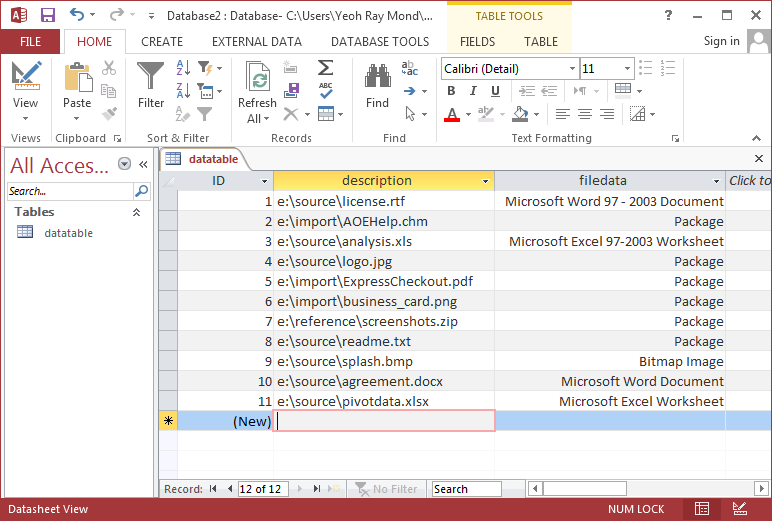
For file names, you can use the FILENAME format specifier to extract only the file name portion from a fully qualified file name. For e.g. the description column below stores fully qualified file names:
 t
t
Using the <description> tag results in errors when the product uses the column value to generate file names:
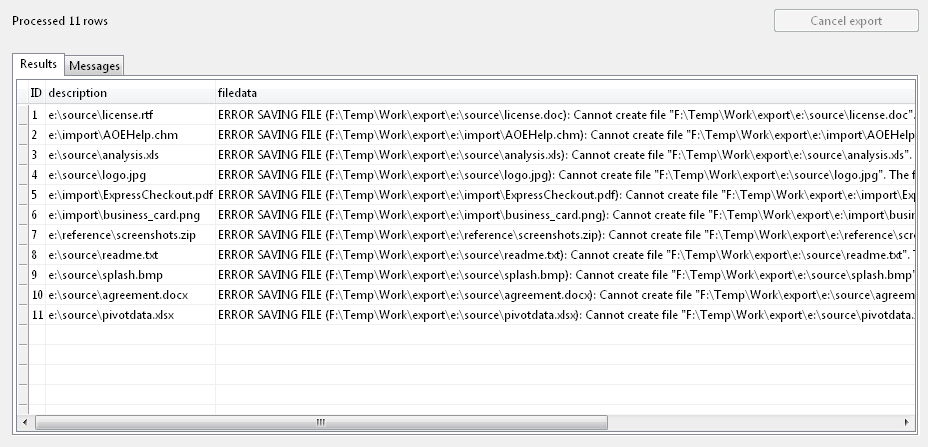
To address this, we append the FILENAME format specifier to the tag e.g.
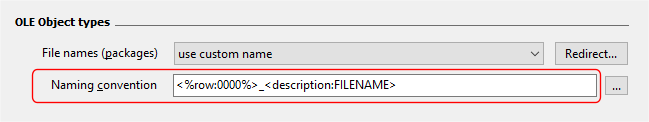
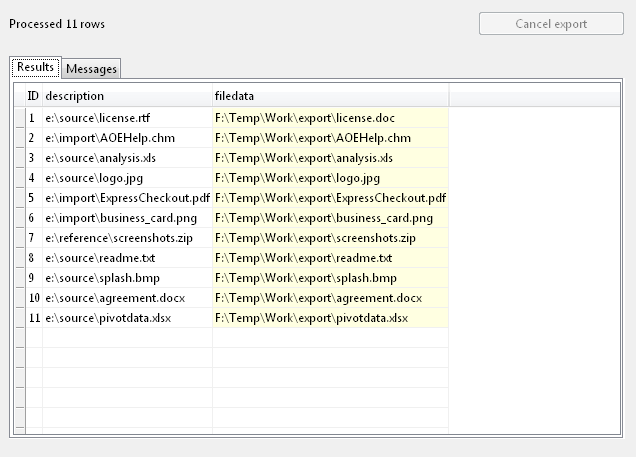
The product now only uses the file name portion of the column value to generate file names i.e.
For numeric values, you can also use a format specifier. E.g. the <%row%> tag is a sequential number of each image that is exported. Using the tag without a format specifier will result in the following values: 1, 2, 3, ... (n). If you want to format the sequence value to 4 digits, prefixed with 0s, you can amend the tag to include the format specified this way: <%row:0000%>. This will then result in the following values: 0001, 0002, 0003, ... (n).
For datetime values retrieved from a database column, you can also use format specifiers to determine how to display the datetime value. The default format is yyyymmdd, so for a datetime value of 31 January 1970, the displayed value is 19700131. See this page for details of the available datetime format specifiers.