If you want to import only files and related file metadata information into your database, you can simply select the Files item as the source data type. You do not need to create a CSV or Excel source data file.
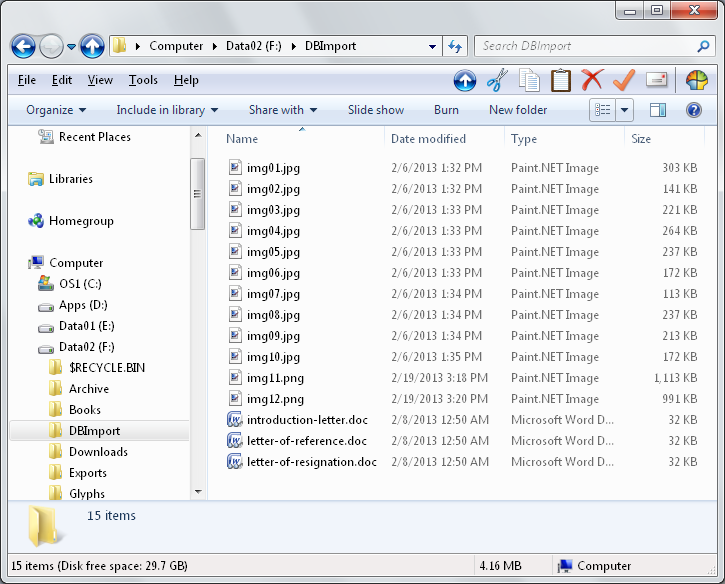
E.g. you want to upload the following files:
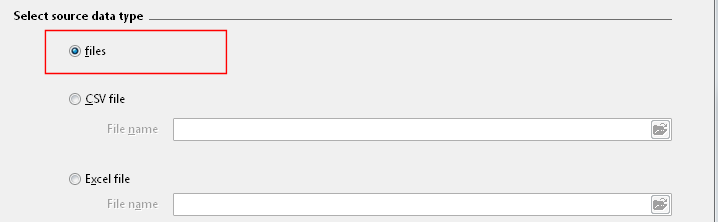
In the Select source data page, select the Files item.
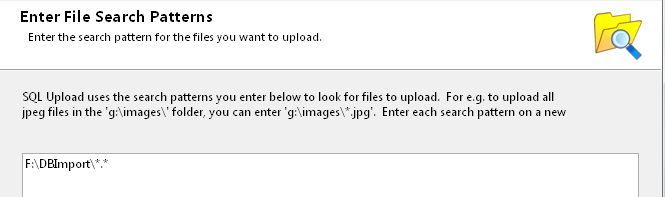
On the next page, enter the file search patterns for the files. In this case, you could use a single wildcard search, which will upload all files in the folder,
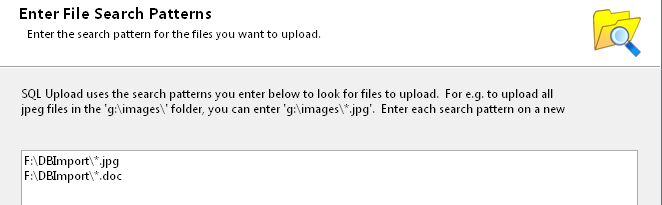
or you could be more specific and use the file extension as a filter, in case you may have other types of files contained in that folder e.g. the system generated thumbnail files.
In the data mapping screen, SQL File Import automatically sets up some default transformations for you.
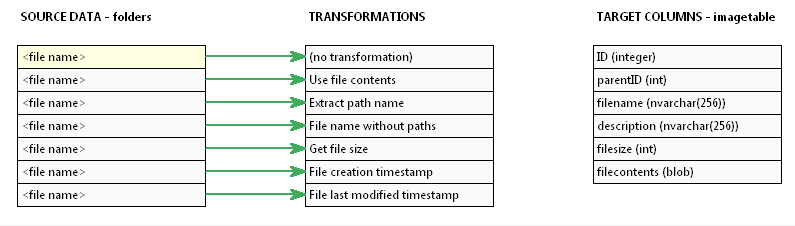
You can see that using just the file name, you can extract quite a bit of details using scripts. In this example, we want to map 4 values to our target table. First is the fully qualified file name itself:
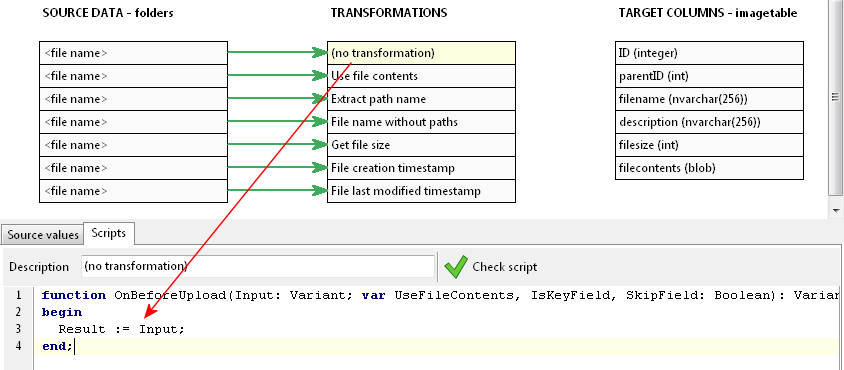
Since we want to take the complete value, the script just assigns the input value to the output (result) value. Next is the file contents.
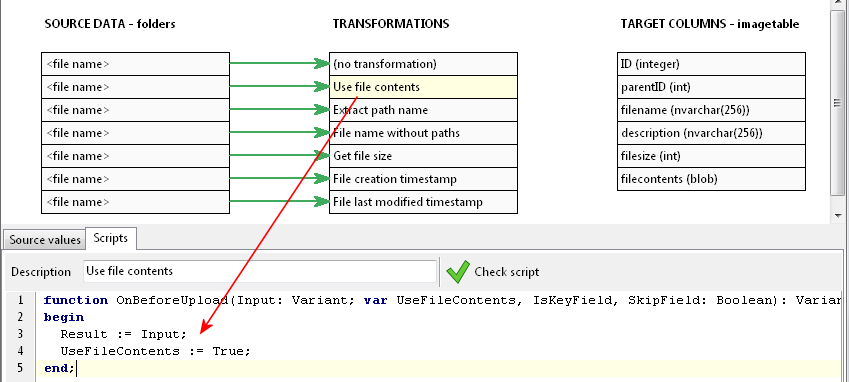
Here, our output (result) value is also the fully qualified file name, but now, we are setting the UseFileContents value to true. This makes SQL File Import upload the contents of the file itself, instead of the file name. Next, we want to upload just the file name itself.
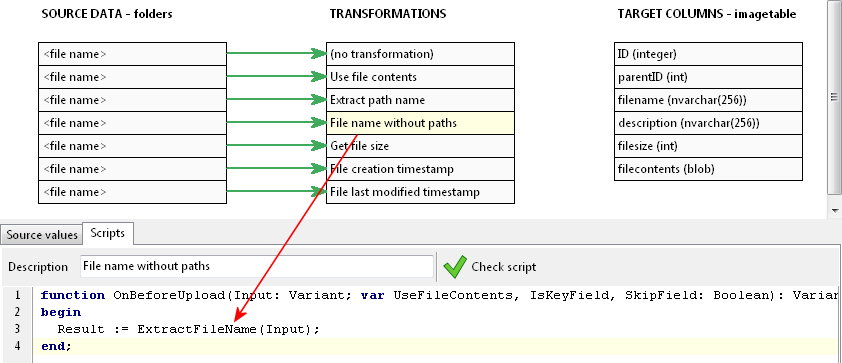
This is done by using the ExtractFileName function, and assigning the result to the output (result) value. Lastly, we want to upload the file size.
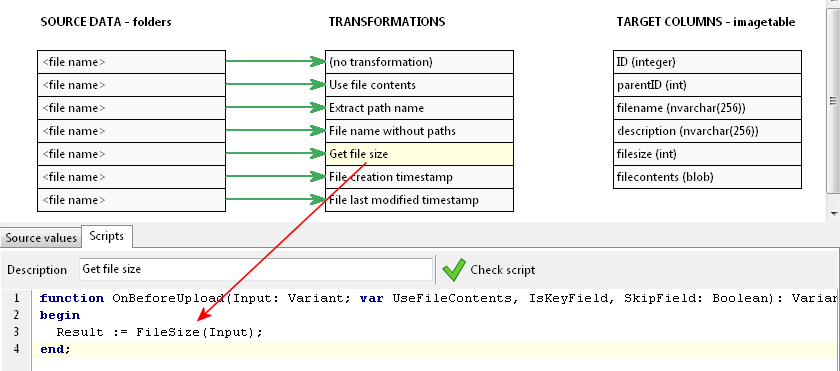
This is done by using the FileSize function.
After that, we just map the columns to the target columns.
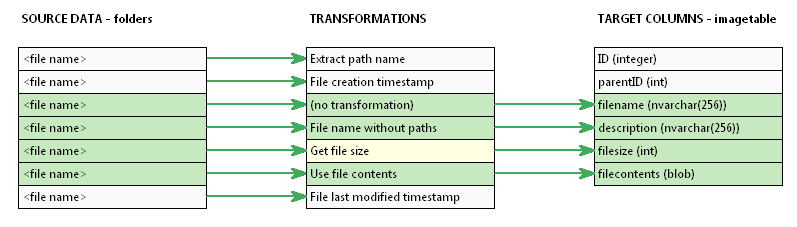
On the next page, SQL File Import will run the upload script, and you can check how the values have mapped to the target columns.
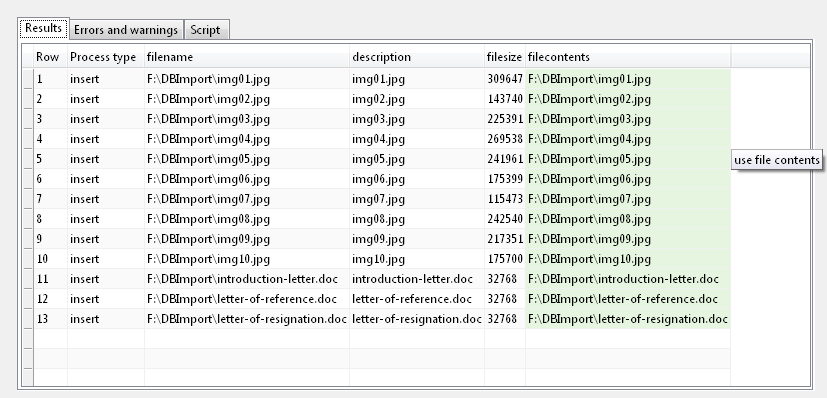
The filecontents column is displayed with a green background to indicate that the contents of the file in that column will be imported, and not the value itself.
For a list of all file-related functions, see this topic.