|
Introduction |
 |
Using SQL Spreadsheets |
|
|
Define column formats
SQL
Spreadsheets uses the default Excel formatting type for all
columns, except for date/time data, where it uses the yyyy-mm-dd
hh:mm:ss format.
|
|
Note
that for numbers, you must use ,
as the
thousands separator, and .
as the
decimal separator, when defining the column formats in SQL
Spreadsheets. Excel will use the correct separators based on your
regional settings, but the format type you enter in SQL
Spreadsheets must use ,
and
.
as the
thousands and decimal separators respectively.
|
|
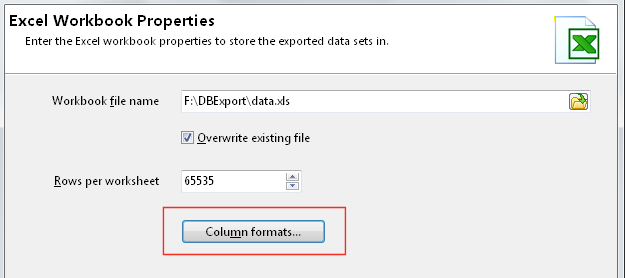
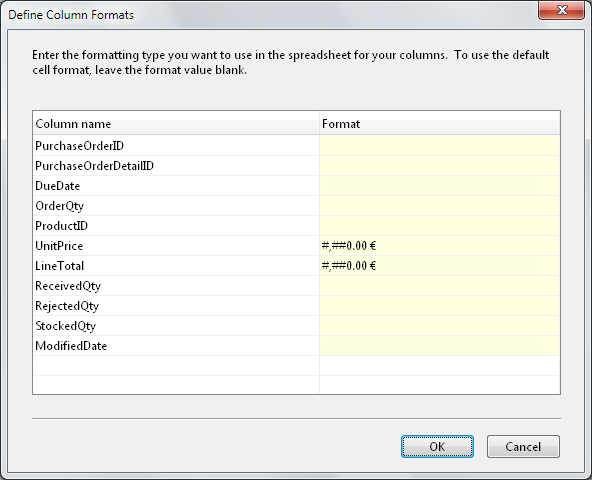
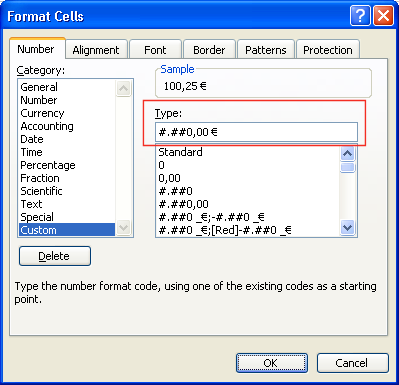
If you want to define a different format for your columns, click on
the Column
formats button.
Enter the format type you want to use. If you want to use the
General
Excel
format type, leave the format value blank. In the example below, we
want to use the #.##0,00
€ format
type for the UnitPrice
and
LineTotal
columns.
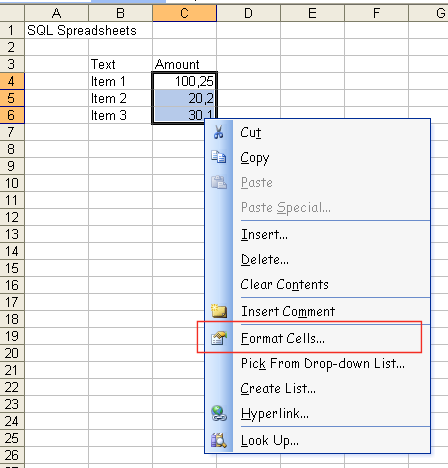
To find out the Excel format type, you can use Excel to first enter
some test values, then select the Format
Cells item.
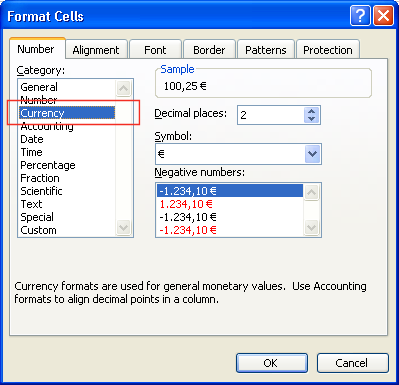
Select the format type you want to use.
Click on the Custom
option
to see how the format type is defined. Use this same value in SQL
Spreadsheets, except for numbers, where you must use ,
as the
thousands separator and .
as the
decimal separator.
|